Protecting Your Loved Ones
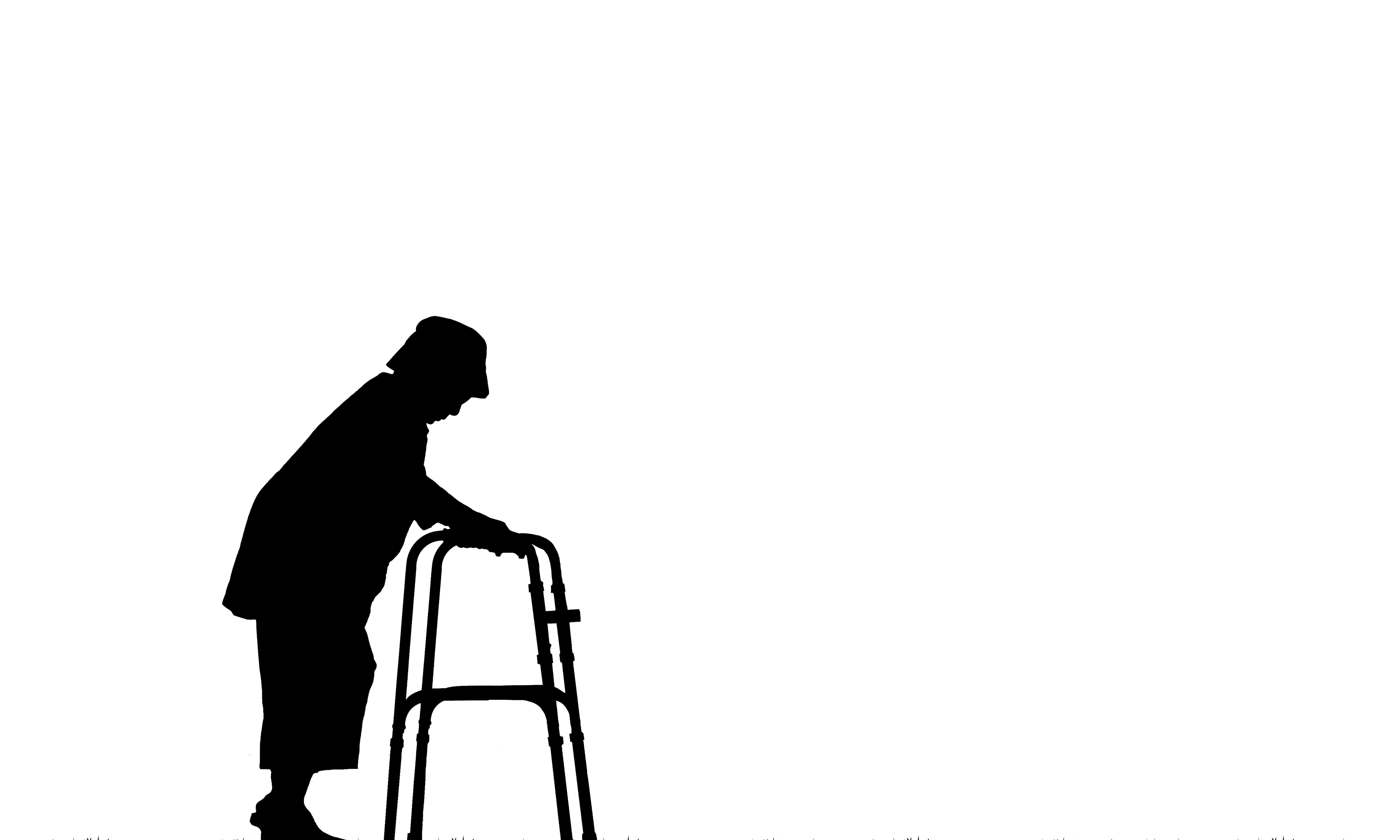
Deciding to place an elderly parent or incapacitated loved one in a nursing home is never easy. Families often make this choice with the hope that trained professionals will provide a safer and more supportive environment than can be offered at home. Unfortunately, even in licensed facilities, nursing home residents face serious risks — especially falls and preventable injuries that can result from staff negligence or poor management.
The Scope of Nursing Home Falls
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 75% of nursing home residents fall each year. Even more alarming, many residents fall more than once within a twelve-month period. Of these incidents, almost 2,000 falls annually result in fatalities. These statistics reveal that falls are not isolated accidents but a recurring and systemic problem in long-term care facilities.
Why Nursing Home Falls Happen
Many nursing homes are understaffed or fail to provide adequate supervision for their residents. Some of the most common causes of falls and elder injuries include:
- Understaffing: Fewer caregivers means less monitoring of frail residents, increasing fall risks.
- Poor training: Staff may not be properly trained in assisting residents with mobility or in fall-prevention techniques.
- Environmental hazards: Wet floors, poor lighting, loose rugs, or cluttered hallways create dangerous conditions.
- Medication errors: Incorrect prescriptions or dosages can cause dizziness, weakness, or confusion that leads to falls.
- Low staff morale: Poor pay and stressful conditions often result in negligent or inattentive care.
These factors are not excuses — they are signs of neglect. Nursing home operators have a legal duty to protect residents from foreseeable harm.
Other Common Nursing Home Injuries
Falls are not the only dangers residents face in long-term care facilities. Families should also be aware of other common injuries and incidents, including:
- Bedsores (Pressure Ulcers): Often a result of leaving immobile residents in one position for too long without proper care.
- Medication Accidents: Incorrect medications or missed doses can have life-threatening consequences.
- Elder Abuse: Physical, emotional, or even financial abuse by poorly trained or unsupervised staff.
- Infections: Unsanitary conditions and lack of proper hygiene practices can lead to dangerous infections.
Legal Responsibility and Nursing Home Negligence
Nursing homes are licensed by their state and must meet certain standards to qualify for Medicare or Medicaid billing. Routine inspections often reveal violations that can put residents at risk. When facilities fail to correct these violations, they may be held legally liable for negligence. Victims and their families may pursue compensation through a personal injury lawsuit or, in cases of wrongful death, a wrongful death claim.
What Families Should Do if Neglect is Suspected
If you suspect that your loved one’s fall or injury was caused by nursing home negligence, immediate action is critical:
- 📋 Document everything — injuries, conditions in the facility, and staff behavior.
- 📸 Take photos and videos of hazards or visible injuries.
- 👩⚕️ Seek medical evaluation for your loved one from an independent physician.
- ⚖️ Consult an attorney experienced in elder injury and nursing home negligence cases.
- 📞 Report the facility to your state’s licensing board or local adult protective services.
Taking action not only protects your loved one but also helps prevent similar harm to other residents.
Compensation for Nursing Home Injuries
Victims of nursing home negligence may be entitled to compensation for:
- Medical expenses and rehabilitation
- Pain and suffering
- Emotional distress
- Loss of quality of life
- Funeral expenses in wrongful death cases
💼 Protect Your Loved Ones From Nursing Home Negligence
No family should have to watch their loved one suffer because of poor care in a nursing home. Attorney Art Majlessi has decades of experience representing families in personal injury and wrongful death cases involving nursing home neglect and elder injuries.
- ⚖️ Proven record in nursing home negligence litigation
- 📅 Free consultation to discuss your case
- 💰 No legal fees unless we win
📞 Call (310) 724-6222 or (415) 629-0109
📨 Or submit your case online today to speak with California’s trusted elder injury attorney.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Please consult with a licensed attorney regarding your specific situation.